Dealing with Time
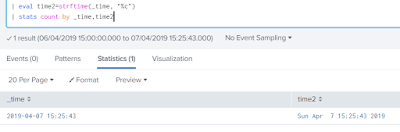
Dealing with Time: Its extremely important to have a proper timestamp. It helps to have all the events organized. _time is a default field and is present in all the events. In cases where an event doesn't contain a timestamp, Splunk automatically assign a timestamp value to the event when the event was indexed. Refrain from using "All Time", reason being it will really be a very heavy task for Splunk to have all the data in place and then to apply your SPL over it. Time conversion and its usage: There is a function called now(), which takes no arguments and returns the time when the search was started. Another add-on in Splunk is, we have an ability to convert and use time based on our requirements. For doing so we can use eval function followed by few functions: strftime(X, Y) This will convert an epoch timestamp (X) into a string format described by Y (Example: To showcase time based on our requirements). strptime(X, Y) This will convert a strin...